
Respiratory diseases in animals can vary widely depending on the species. Common respiratory issues include infections like pneumonia, bronchitis, and kennel cough in dogs, respiratory infections in cats, and respiratory distress syndrome in livestock such as pigs. These conditions can be caused by viruses, bacteria, fungi, or environmental factors like poor air quality or allergens. Early detection and proper treatment are crucial for managing respiratory diseases in animals.
Animal Raspiratory diseases
Add a header to begin generating the table of contents
Respiratory diseases in animals encompass a range of conditions, including:
- Pneumonia: Inflammation of the lungs often caused by bacterial, viral, or fungal infections.
- Bronchitis: Inflammation of the bronchial tubes leading to coughing and difficulty breathing.
- Kennel Cough: Highly contagious respiratory infection in dogs caused by various viruses and bacteria.
- Feline Upper Respiratory Infections: Common in cats and caused by viruses like feline herpesvirus and feline calicivirus.
- Equine Respiratory Diseases: Including conditions like equine influenza, strangles, and equine herpesvirus.
- Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Seen in livestock such as pigs, often due to environmental stressors or infections.
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): Seen in horses and other animals, characterized by airway inflammation and obstruction.
- Aspiration Pneumonia: Occurs when animals inhale foreign material into their lungs, leading to inflammation and infection.
- Allergic Respiratory Diseases: Some animals may develop respiratory issues due to allergies to dust, pollen, or other environmental factors.
These are just a few examples, and there are many other respiratory diseases that affect animals depending on their species, environment, and other factors.
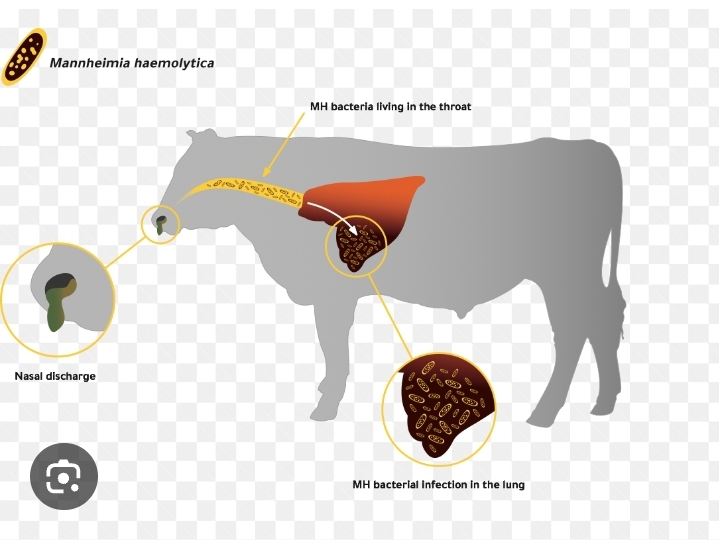
Causes of Respiratory infection
Understanding and addressing these underlying causes are essential for preventing and managing respiratory diseases in animals.
Respiratory diseases in animals can be caused by various factors, including:
- Infectious Agents: Viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites can all cause respiratory infections in animals. Examples include canine distemper virus, feline herpesvirus, mycoplasma bacteria, and Aspergillus fungi.
- Environmental Factors: Poor air quality, exposure to pollutants, dust, smoke, and allergens can irritate the respiratory tract and lead to respiratory diseases.
- Stress: Stress weakens the immune system, making animals more susceptible to respiratory infections. Factors like overcrowding, transportation, and changes in environment can contribute to stress-induced respiratory issues.
- Poor Husbandry Practices: Inadequate ventilation, overcrowding, improper nutrition, and unsanitary living conditions can predispose animals to respiratory diseases.
- Genetics: Some animals may be genetically predisposed to certain respiratory conditions, making them more susceptible to developing respiratory diseases.
- Aspiration: Accidental inhalation of food, water, or other foreign material into the respiratory tract can lead to aspiration pneumonia.
- Trauma: Injuries to the respiratory system, such as fractures of the ribs or damage to the airways, can predispose animals to respiratory diseases or complications.
- Immune System Disorders: Animals with weakened immune systems due to underlying diseases or conditions may be more prone to respiratory infections.
- Exposure to Contaminated Sources: Animals may contract respiratory diseases from exposure to contaminated food, water, bedding, or other sources.
Clinical sign of Raspiratory:
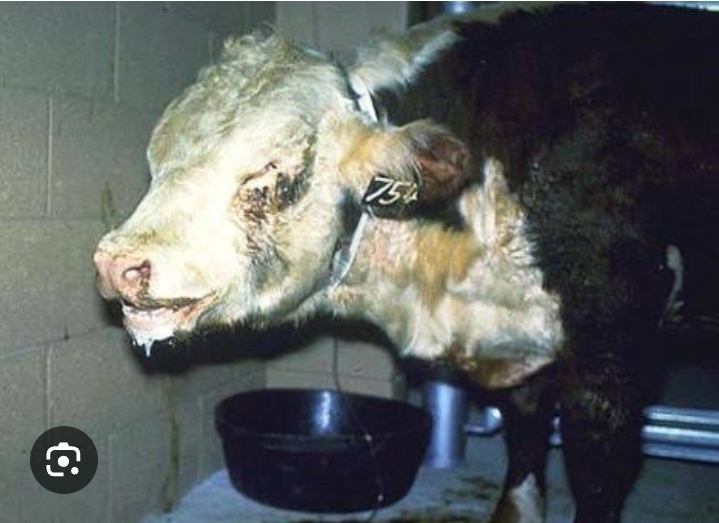
The clinical signs of respiratory disease in animals can vary depending on the specific condition and the species affected. However, common signs may include:
- Coughing: Persistent or intermittent coughing is a common symptom of respiratory disease in animals.
- Sneezing: Frequent sneezing may indicate irritation or infection in the nasal passages or upper respiratory tract.
- Nasal Discharge: Discharge from the nose, which can be clear, mucoid, or purulent (pus-like), may indicate infection or inflammation.
- Labored Breathing: Difficulty breathing, rapid breathing, or open-mouth breathing can suggest respiratory distress.
- Wheezing or Noisy Breathing: Wheezing sounds or other abnormal respiratory noises may indicate airway obstruction or inflammation.
- Cyanosis: Bluish discoloration of the mucous membranes, particularly the gums and tongue, can indicate poor oxygenation of the blood.
- Decreased Activity or Exercise Intolerance: Animals with respiratory disease may show reduced energy levels or reluctance to engage in physical activity due to difficulty breathing.
- Fever: Elevated body temperature may accompany respiratory infections, although it is not always present.
- Loss of Appetite: Respiratory illness can cause animals to lose interest in food due to discomfort or difficulty breathing.
- Postural Changes: Animals may assume specific postures to facilitate breathing, such as extending the neck or standing with the elbows abducted (outward).
- Weight Loss: Chronic respiratory conditions can lead to weight loss over time due to decreased appetite and increased energy expenditure.
- Lethargy: Animals with respiratory disease may appear tired or lethargic due to reduced oxygenation and discomfort.
These signs can vary in severity and may not all be present in every case. Prompt veterinary evaluation is essential if any respiratory symptoms are observed in animals, as early diagnosis and treatment can improve outcomes.
Treatment and Medication of the disease:
The treatment of respiratory diseases in animals depends on the specific condition and its underlying cause. In general, some approaches to managing respiratory diseases in animals include:
- Medication: Antibiotics may be prescribed for bacterial infections, while antiviral or antifungal medications may be necessary for viral or fungal infections, respectively. Anti-inflammatory drugs such as corticosteroids can help reduce inflammation in the respiratory tract.
- Supportive Care: This may include providing supplemental oxygen, maintaining hydration, and ensuring adequate nutrition to support the animal’s immune system during recovery.
- Environmental Management: Improving ventilation, reducing exposure to pollutants or allergens, and maintaining clean living conditions can help prevent respiratory diseases and support recovery.
- Quarantine and Isolation: Infected animals should be separated from healthy individuals to prevent the spread of contagious respiratory diseases.
- Fluid Therapy: Intravenous or subcutaneous fluids may be administered to animals with severe respiratory distress to maintain hydration and electrolyte balance.
- Respiratory Therapy: Nebulization or aerosol therapy may be used to deliver medications directly to the respiratory tract, helping to alleviate symptoms and improve lung function.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove obstructions or repair structural abnormalities in the respiratory tract.
- Preventive Measures: Vaccination against common respiratory pathogens can help prevent certain respiratory diseases in animals.
It’s important to note that while many respiratory diseases can be managed effectively with appropriate treatment, some may require long-term management or may have a guarded prognosis. Early detection, accurate diagnosis, and prompt veterinary intervention are crucial for the successful management of respiratory diseases in animals.

Leave a Reply