
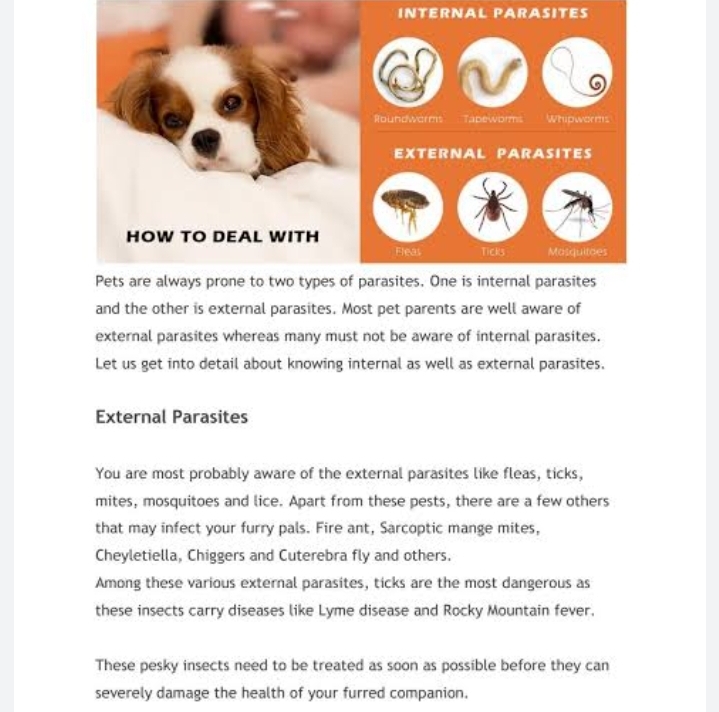
The epidiology of the Ticks and mites in Animals:
Tick fever infections are caused by various pathogens transmitted through tick bites, leading to different diseases depending on the specific pathogen. Some common tick-borne diseases include Lyme disease, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, tick-borne encephalitis, Ehrlichiosis, Anaplasmosis, and Babesiosis.
Causes of Tick Fever Infections
Tick fever infections are caused by bacteria, viruses, or parasites transmitted when an infected tick bites a human or animal. The tick becomes infected by feeding on the blood of an infected host (such as a bird or rodent) and then passes the pathogen to the next host it feeds on.
Symptoms of Tick Fever Infections
Symptoms vary depending on the specific disease but commonly include:
- Fever
- Headache
- Fatigue
- Muscle and joint aches
- Rash (which can differ in appearance)
- Chills
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Nausea and vomiting
- Neurological symptoms (in severe cases)
Diseases Caused by Tick Fever Infections
Some of the diseases caused by tick-borne pathogens include:
- Lyme disease: Caused by Borrelia burgdorferi bacteria.
- Rocky Mountain spotted fever (RMSF): Caused by Rickettsia rickettsii bacteria.
- Tick-borne encephalitis (TBE): Caused by the tick-borne encephalitis virus.
- Ehrlichiosis: Caused by Ehrlichia bacteria.
- Anaplasmosis: Caused by Anaplasma phagocytophilum bacterial.
- Babesiosis: Caused by Babesia parasites.
Treatment of Tick Fever Infections
Treatment varies based on the specific disease:
- Antibiotics: Used for bacterial infections like Lyme disease and RMSF. Early treatment is crucial.
- Antiviral Medications: Sometimes used for viral infections like TBE.

- Symptomatic Treatment: Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications may be used to manage symptoms.
- Hospitalization: May be necessary for severe cases.
- Supportive Care: Includes hydration, rest, and monitoring.
Prevention
Preventing tick bites is key to avoiding tick fever infections. This includes using insect repellents, wearing protective clothing, and regularly checking for ticks after spending time in areas where ticks are common.
Also Read about Nedbank Job Opportunity
The medications and treatment for tick fever infections vary depending on the specific disease contracted.
Here are some common approaches:
Antibiotics: For bacterial infections like Lyme disease and Rocky Mountain spotted fever, antibiotics are typically prescribed.
The specific antibiotic and duration of treatment depend on the severity of the infection and the patient’s age and medical history.
Antiviral Medications: In the case of tick-borne viral infections such as tick-borne encephalitis, antiviral medications may be used to manage symptoms and reduce the severity of the illness.
Symptomatic Treatment: Treatment may also include medications to alleviate symptoms such as fever, pain, and inflammation. Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen may be recommended.
Hospitalization: In severe cases or if complications arise, hospitalization may be necessary. This is particularly true for diseases like Rocky Mountain spotted fever, which can lead to serious complications if not treated promptly.
Supportive Care: Patients with tick fever infections may require supportive care to manage symptoms and prevent complications. This may include intravenous fluids for hydration, rest, and close monitoring of vital signs.
Prevention of Future Infections: After recovering from a tick fever infection, it’s essential to take steps to prevent future tick bites. This includes using insect repellents, wearing protective clothing, and performing regular tick checks.

Leave a Reply